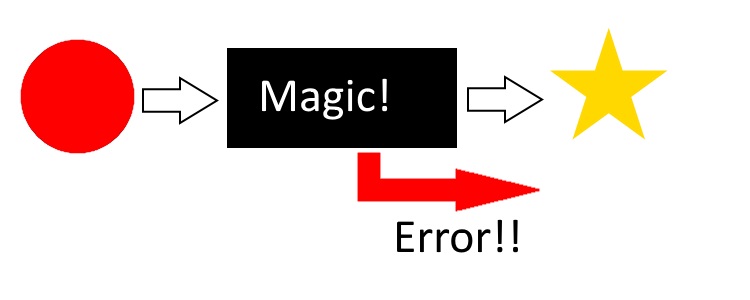
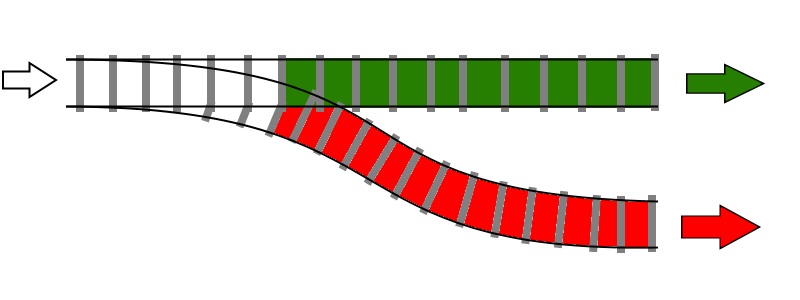
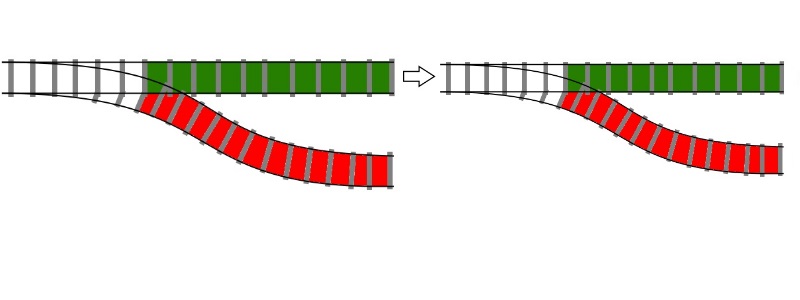
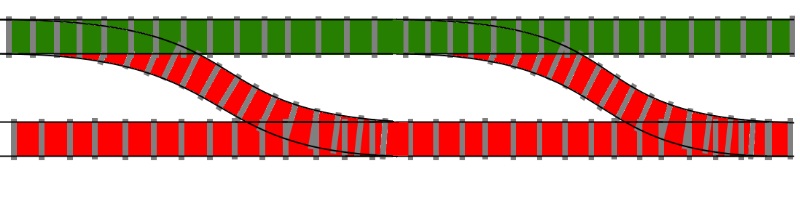
val thisIsAnInt : int
Full name: index.thisIsAnInt
Full name: index.thisIsAnInt
val thisIsAString : string
Full name: index.thisIsAString
Full name: index.thisIsAString
val optionalTypeAnnotation : bool
Full name: index.optionalTypeAnnotation
Full name: index.optionalTypeAnnotation
type bool = System.Boolean
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.bool
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.bool
val listOfFloats : float list
Full name: index.listOfFloats
Full name: index.listOfFloats
val arrayOfStrings : string []
Full name: index.arrayOfStrings
Full name: index.arrayOfStrings
val add : a:int -> b:int -> int
Full name: index.add
Full name: index.add
val a : int
val b : int
val sign : num:int -> string
Full name: index.sign
Full name: index.sign
val num : int
val fib : n:int -> int
Full name: index.fib
Full name: index.fib
val n : int
val printer : f:float -> unit
Full name: index.printer
Full name: index.printer
val f : float
val printfn : format:Printf.TextWriterFormat<'T> -> 'T
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.ExtraTopLevelOperators.printfn
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.ExtraTopLevelOperators.printfn
Multiple items
module List
from Microsoft.FSharp.Collections
--------------------
type List<'T> =
| ( [] )
| ( :: ) of Head: 'T * Tail: 'T list
interface IEnumerable
interface IEnumerable<'T>
member GetSlice : startIndex:int option * endIndex:int option -> 'T list
member Head : 'T
member IsEmpty : bool
member Item : index:int -> 'T with get
member Length : int
member Tail : 'T list
static member Cons : head:'T * tail:'T list -> 'T list
static member Empty : 'T list
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List<_>
module List
from Microsoft.FSharp.Collections
--------------------
type List<'T> =
| ( [] )
| ( :: ) of Head: 'T * Tail: 'T list
interface IEnumerable
interface IEnumerable<'T>
member GetSlice : startIndex:int option * endIndex:int option -> 'T list
member Head : 'T
member IsEmpty : bool
member Item : index:int -> 'T with get
member Length : int
member Tail : 'T list
static member Cons : head:'T * tail:'T list -> 'T list
static member Empty : 'T list
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List<_>
val filter : predicate:('T -> bool) -> list:'T list -> 'T list
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.filter
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.filter
val i : float
val map : mapping:('T -> 'U) -> list:'T list -> 'U list
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.map
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.map
val iter : action:('T -> unit) -> list:'T list -> unit
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.iter
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.iter
val value : 'a
val fn : ('a -> 'b)
type User =
{FirstName: string;
LastName: string;
Age: int;}
Full name: index.User
{FirstName: string;
LastName: string;
Age: int;}
Full name: index.User
User.FirstName: string
Multiple items
val string : value:'T -> string
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.string
--------------------
type string = System.String
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.string
val string : value:'T -> string
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.string
--------------------
type string = System.String
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.string
User.LastName: string
User.Age: int
Multiple items
val int : value:'T -> int (requires member op_Explicit)
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.int
--------------------
type int = int32
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.int
--------------------
type int<'Measure> = int
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.int<_>
val int : value:'T -> int (requires member op_Explicit)
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.int
--------------------
type int = int32
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.int
--------------------
type int<'Measure> = int
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.int<_>
val kai : User
Full name: index.kai
Full name: index.kai
val cloneOfKai : User
Full name: index.cloneOfKai
Full name: index.cloneOfKai
val olderKai : User
Full name: index.olderKai
Full name: index.olderKai
type Shape =
| Rectangle of width: float * length: float
| Circle of radius: float
| Triangle of float * float * float
Full name: index.Shape
| Rectangle of width: float * length: float
| Circle of radius: float
| Triangle of float * float * float
Full name: index.Shape
union case Shape.Rectangle: width: float * length: float -> Shape
Multiple items
val float : value:'T -> float (requires member op_Explicit)
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.float
--------------------
type float = System.Double
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.float
--------------------
type float<'Measure> = float
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.float<_>
val float : value:'T -> float (requires member op_Explicit)
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.float
--------------------
type float = System.Double
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.float
--------------------
type float<'Measure> = float
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.float<_>
union case Shape.Circle: radius: float -> Shape
union case Shape.Triangle: float * float * float -> Shape
val rectangle : Shape
Full name: index.rectangle
Full name: index.rectangle
val circle : Shape
Full name: index.circle
Full name: index.circle
val triangle : Shape
Full name: index.triangle
Full name: index.triangle
val whichShape : shape:Shape -> unit
Full name: index.whichShape
Full name: index.whichShape
val shape : Shape
val width : float
val length : float
val radius : float
val side1 : float
val side2 : float
val side3 : float
Multiple items
module Option
from Microsoft.FSharp.Core
--------------------
type Option<'a> =
| Some of 'a
| None
Full name: index.Option<_>
module Option
from Microsoft.FSharp.Core
--------------------
type Option<'a> =
| Some of 'a
| None
Full name: index.Option<_>
union case Option.Some: 'a -> Option<'a>
union case Option.None: Option<'a>
val validString : string option
Full name: index.validString
Full name: index.validString
type 'T option = Option<'T>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.option<_>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.option<_>
val invalidString : string option
Full name: index.invalidString
Full name: index.invalidString
val words : string list
Full name: index.words
Full name: index.words
val foundWord : string option
Full name: index.foundWord
Full name: index.foundWord
val tryFind : predicate:('T -> bool) -> list:'T list -> 'T option
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.tryFind
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.tryFind
val x : string
val missingWord : string option
Full name: index.missingWord
Full name: index.missingWord
val printString : input:Option<string> -> unit
Full name: index.printString
Full name: index.printString
val input : Option<string>
val s : string
type ContactUser =
{Username: string;
Email: string option;
PhoneNumber: string option;}
Full name: index.ContactUser
{Username: string;
Email: string option;
PhoneNumber: string option;}
Full name: index.ContactUser
ContactUser.Username: string
ContactUser.Email: string option
ContactUser.PhoneNumber: string option
val createUser : username:'a -> emailAddress:'b -> phoneNumber:'c -> ContactUser
Full name: index.createUser
Full name: index.createUser
val username : 'a
val emailAddress : 'b
val phoneNumber : 'c
type ContactInformation =
| Email of string
| PhoneNumber of string
| EmailAndPhone of string * string
Full name: index.ContactInformation
| Email of string
| PhoneNumber of string
| EmailAndPhone of string * string
Full name: index.ContactInformation
union case ContactInformation.Email: string -> ContactInformation
union case ContactInformation.PhoneNumber: string -> ContactInformation
union case ContactInformation.EmailAndPhone: string * string -> ContactInformation
type SafeContactUser =
{Username: string;
Contact: ContactInformation;}
Full name: index.SafeContactUser
{Username: string;
Contact: ContactInformation;}
Full name: index.SafeContactUser
SafeContactUser.Username: string
SafeContactUser.Contact: ContactInformation
val email : ContactInformation
Full name: index.email
Full name: index.email
val phoneNumber : ContactInformation
Full name: index.phoneNumber
Full name: index.phoneNumber
val emailAndPhone : ContactInformation
Full name: index.emailAndPhone
Full name: index.emailAndPhone
val user1 : SafeContactUser
Full name: index.user1
Full name: index.user1
val user2 : SafeContactUser
Full name: index.user2
Full name: index.user2
val user3 : SafeContactUser
Full name: index.user3
Full name: index.user3
val user4 : SafeContactUser
Full name: index.user4
Full name: index.user4
val user5 : SafeContactUser
Full name: index.user5
Full name: index.user5
val parseDateTime : dateTime:string -> 'a
Full name: index.parseDateTime
Full name: index.parseDateTime
val dateTime : string
val getYear : date:System.DateTime -> int
Full name: index.getYear
Full name: index.getYear
val date : System.DateTime
namespace System
Multiple items
type DateTime =
struct
new : ticks:int64 -> DateTime + 10 overloads
member Add : value:TimeSpan -> DateTime
member AddDays : value:float -> DateTime
member AddHours : value:float -> DateTime
member AddMilliseconds : value:float -> DateTime
member AddMinutes : value:float -> DateTime
member AddMonths : months:int -> DateTime
member AddSeconds : value:float -> DateTime
member AddTicks : value:int64 -> DateTime
member AddYears : value:int -> DateTime
...
end
Full name: System.DateTime
--------------------
System.DateTime()
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(ticks: int64) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(ticks: int64, kind: System.DateTimeKind) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, calendar: System.Globalization.Calendar) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int, kind: System.DateTimeKind) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int, calendar: System.Globalization.Calendar) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int, millisecond: int) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int, millisecond: int, kind: System.DateTimeKind) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
type DateTime =
struct
new : ticks:int64 -> DateTime + 10 overloads
member Add : value:TimeSpan -> DateTime
member AddDays : value:float -> DateTime
member AddHours : value:float -> DateTime
member AddMilliseconds : value:float -> DateTime
member AddMinutes : value:float -> DateTime
member AddMonths : months:int -> DateTime
member AddSeconds : value:float -> DateTime
member AddTicks : value:int64 -> DateTime
member AddYears : value:int -> DateTime
...
end
Full name: System.DateTime
--------------------
System.DateTime()
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(ticks: int64) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(ticks: int64, kind: System.DateTimeKind) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, calendar: System.Globalization.Calendar) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int, kind: System.DateTimeKind) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int, calendar: System.Globalization.Calendar) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int, millisecond: int) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
System.DateTime(year: int, month: int, day: int, hour: int, minute: int, second: int, millisecond: int, kind: System.DateTimeKind) : unit
(+0 other overloads)
property System.DateTime.Year: int
val date : System.DateTime
Full name: index.date
Full name: index.date
val currentYear : int
Full name: index.currentYear
Full name: index.currentYear
val composedGetYear : (string -> int)
Full name: index.composedGetYear
Full name: index.composedGetYear
val yearFromComposed : int
Full name: index.yearFromComposed
Full name: index.yearFromComposed
val add : x:int -> y:int -> int
Full name: index.add
Full name: index.add
val x : int
val y : int
val threeParams : firstName:'a -> middleName:'b -> lastName:'c -> unit
Full name: index.threeParams
Full name: index.threeParams
val firstName : 'a
val middleName : 'b
val lastName : 'c
val curriedAdd : (int -> int)
Full name: index.curriedAdd
Full name: index.curriedAdd
Multiple items
val double : (int -> int)
Full name: index.double
--------------------
type double = System.Double
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.double
val double : (int -> int)
Full name: index.double
--------------------
type double = System.Double
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.double
val sum : list:int list -> int
Full name: index.sum
Full name: index.sum
Multiple items
val list : int list
--------------------
type 'T list = List<'T>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.list<_>
val list : int list
--------------------
type 'T list = List<'T>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.list<_>
val reduce : reduction:('T -> 'T -> 'T) -> list:'T list -> 'T
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.reduce
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.reduce
val freeSum : (int list -> int)
Full name: index.freeSum
Full name: index.freeSum
val batchesOf : n:int -> (seq<'a> -> seq<seq<'a>>)
Full name: index.batchesOf
Full name: index.batchesOf
module Seq
from Microsoft.FSharp.Collections
from Microsoft.FSharp.Collections
val mapi : mapping:(int -> 'T -> 'U) -> source:seq<'T> -> seq<'U>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.Seq.mapi
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.Seq.mapi
val i : int
val v : 'a
val groupBy : projection:('T -> 'Key) -> source:seq<'T> -> seq<'Key * seq<'T>> (requires equality)
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.Seq.groupBy
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.Seq.groupBy
val fst : tuple:('T1 * 'T2) -> 'T1
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.fst
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.fst
val map : mapping:('T -> 'U) -> source:seq<'T> -> seq<'U>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.Seq.map
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.Seq.map
val snd : tuple:('T1 * 'T2) -> 'T2
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.snd
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.Operators.snd
val doubleAndIncrement : x:int -> int
Full name: index.doubleAndIncrement
Full name: index.doubleAndIncrement
val freeDoubleAndIncrement : (int -> int)
Full name: index.freeDoubleAndIncrement
Full name: index.freeDoubleAndIncrement
val result : string list * int
Full name: index.result
Full name: index.result
val async : AsyncBuilder
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.ExtraTopLevelOperators.async
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.ExtraTopLevelOperators.async
val username : string
val replies : string list
type 'T list = List<'T>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.list<_>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.list<_>
val count : int
val length : list:'T list -> int
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.length
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.List.length
Multiple items
type Async
static member AsBeginEnd : computation:('Arg -> Async<'T>) -> ('Arg * AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * (IAsyncResult -> 'T) * (IAsyncResult -> unit)
static member AwaitEvent : event:IEvent<'Del,'T> * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T> (requires delegate and 'Del :> Delegate)
static member AwaitIAsyncResult : iar:IAsyncResult * ?millisecondsTimeout:int -> Async<bool>
static member AwaitTask : task:Task -> Async<unit>
static member AwaitTask : task:Task<'T> -> Async<'T>
static member AwaitWaitHandle : waitHandle:WaitHandle * ?millisecondsTimeout:int -> Async<bool>
static member CancelDefaultToken : unit -> unit
static member Catch : computation:Async<'T> -> Async<Choice<'T,exn>>
static member FromBeginEnd : beginAction:(AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * endAction:(IAsyncResult -> 'T) * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member FromBeginEnd : arg:'Arg1 * beginAction:('Arg1 * AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * endAction:(IAsyncResult -> 'T) * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member FromBeginEnd : arg1:'Arg1 * arg2:'Arg2 * beginAction:('Arg1 * 'Arg2 * AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * endAction:(IAsyncResult -> 'T) * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member FromBeginEnd : arg1:'Arg1 * arg2:'Arg2 * arg3:'Arg3 * beginAction:('Arg1 * 'Arg2 * 'Arg3 * AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * endAction:(IAsyncResult -> 'T) * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member FromContinuations : callback:(('T -> unit) * (exn -> unit) * (OperationCanceledException -> unit) -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member Ignore : computation:Async<'T> -> Async<unit>
static member OnCancel : interruption:(unit -> unit) -> Async<IDisposable>
static member Parallel : computations:seq<Async<'T>> -> Async<'T []>
static member RunSynchronously : computation:Async<'T> * ?timeout:int * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> 'T
static member Sleep : millisecondsDueTime:int -> Async<unit>
static member Start : computation:Async<unit> * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> unit
static member StartAsTask : computation:Async<'T> * ?taskCreationOptions:TaskCreationOptions * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> Task<'T>
static member StartChild : computation:Async<'T> * ?millisecondsTimeout:int -> Async<Async<'T>>
static member StartChildAsTask : computation:Async<'T> * ?taskCreationOptions:TaskCreationOptions -> Async<Task<'T>>
static member StartImmediate : computation:Async<unit> * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> unit
static member StartWithContinuations : computation:Async<'T> * continuation:('T -> unit) * exceptionContinuation:(exn -> unit) * cancellationContinuation:(OperationCanceledException -> unit) * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> unit
static member SwitchToContext : syncContext:SynchronizationContext -> Async<unit>
static member SwitchToNewThread : unit -> Async<unit>
static member SwitchToThreadPool : unit -> Async<unit>
static member TryCancelled : computation:Async<'T> * compensation:(OperationCanceledException -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member CancellationToken : Async<CancellationToken>
static member DefaultCancellationToken : CancellationToken
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Control.Async
--------------------
type Async<'T>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Control.Async<_>
type Async
static member AsBeginEnd : computation:('Arg -> Async<'T>) -> ('Arg * AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * (IAsyncResult -> 'T) * (IAsyncResult -> unit)
static member AwaitEvent : event:IEvent<'Del,'T> * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T> (requires delegate and 'Del :> Delegate)
static member AwaitIAsyncResult : iar:IAsyncResult * ?millisecondsTimeout:int -> Async<bool>
static member AwaitTask : task:Task -> Async<unit>
static member AwaitTask : task:Task<'T> -> Async<'T>
static member AwaitWaitHandle : waitHandle:WaitHandle * ?millisecondsTimeout:int -> Async<bool>
static member CancelDefaultToken : unit -> unit
static member Catch : computation:Async<'T> -> Async<Choice<'T,exn>>
static member FromBeginEnd : beginAction:(AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * endAction:(IAsyncResult -> 'T) * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member FromBeginEnd : arg:'Arg1 * beginAction:('Arg1 * AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * endAction:(IAsyncResult -> 'T) * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member FromBeginEnd : arg1:'Arg1 * arg2:'Arg2 * beginAction:('Arg1 * 'Arg2 * AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * endAction:(IAsyncResult -> 'T) * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member FromBeginEnd : arg1:'Arg1 * arg2:'Arg2 * arg3:'Arg3 * beginAction:('Arg1 * 'Arg2 * 'Arg3 * AsyncCallback * obj -> IAsyncResult) * endAction:(IAsyncResult -> 'T) * ?cancelAction:(unit -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member FromContinuations : callback:(('T -> unit) * (exn -> unit) * (OperationCanceledException -> unit) -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member Ignore : computation:Async<'T> -> Async<unit>
static member OnCancel : interruption:(unit -> unit) -> Async<IDisposable>
static member Parallel : computations:seq<Async<'T>> -> Async<'T []>
static member RunSynchronously : computation:Async<'T> * ?timeout:int * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> 'T
static member Sleep : millisecondsDueTime:int -> Async<unit>
static member Start : computation:Async<unit> * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> unit
static member StartAsTask : computation:Async<'T> * ?taskCreationOptions:TaskCreationOptions * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> Task<'T>
static member StartChild : computation:Async<'T> * ?millisecondsTimeout:int -> Async<Async<'T>>
static member StartChildAsTask : computation:Async<'T> * ?taskCreationOptions:TaskCreationOptions -> Async<Task<'T>>
static member StartImmediate : computation:Async<unit> * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> unit
static member StartWithContinuations : computation:Async<'T> * continuation:('T -> unit) * exceptionContinuation:(exn -> unit) * cancellationContinuation:(OperationCanceledException -> unit) * ?cancellationToken:CancellationToken -> unit
static member SwitchToContext : syncContext:SynchronizationContext -> Async<unit>
static member SwitchToNewThread : unit -> Async<unit>
static member SwitchToThreadPool : unit -> Async<unit>
static member TryCancelled : computation:Async<'T> * compensation:(OperationCanceledException -> unit) -> Async<'T>
static member CancellationToken : Async<CancellationToken>
static member DefaultCancellationToken : CancellationToken
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Control.Async
--------------------
type Async<'T>
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Control.Async<_>
static member Async.RunSynchronously : computation:Async<'T> * ?timeout:int * ?cancellationToken:System.Threading.CancellationToken -> 'T